Drope shape analysis
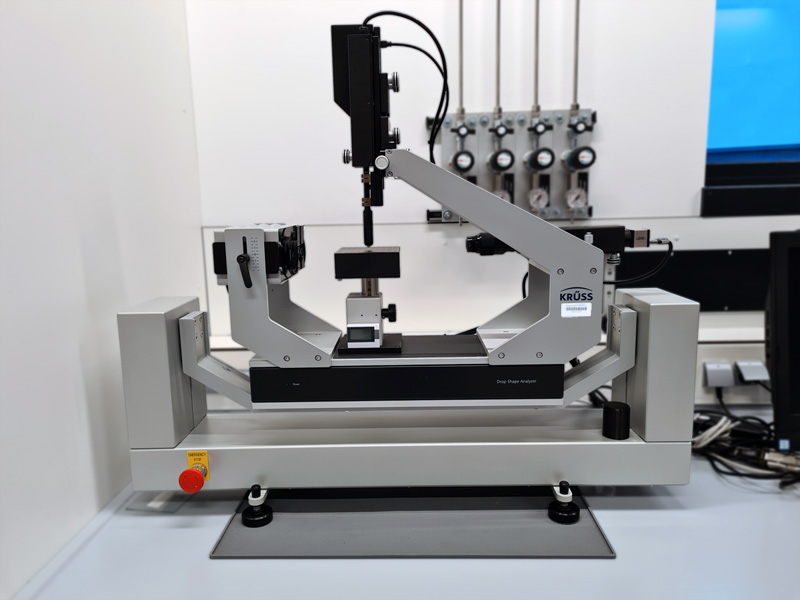
Using the drop shape analysis, the surfaace tension of liquids (handging drop) and the interfacial tension of flat solids (sessile drop) can be measured. The CMP working group of the Department of Chemistry, University of Paderborn, uses a Drop Shape Analyzer by Kruss.
The surface tension of liquids is investigated by the measurement method “hanging drop”. The method can be used both at high and at low surface tensions and is independent of the viscosity. Additionally with this method it is possible to analyse systems with capillary active substances (e.g. surfactants). The surface tension of liquid can be investigated as pure material property or as used for detection of impurities.
The measurement of the interfacial tension of solids can be carried out both statically or dynamically. During the static method the volume of an once generated drop on the surface will not be changed. However, interactions of the droplet with the substrate and the environment (e.g. air) can vary the contact angle:
- The liquid can evaporate.
- The liquid can swell or even dissolve the substrate.
- The liquid and the substrate can react.
- In the material dissolved substances (e.g. sufactants) can migrate into the other phase.
In contrast to the dynamic measurement, the injection capillary does not remain in the droplet during the static measurement and thus cannot affect the contact angle (especially important for small drops).
The dynamic measurement distinguishes between the advancing and the receding angle. The advancing angle simulates the wetting of substrates and therefore gives meaningful values of the free surface energy. The difference between advancing and receding contact angle can provide information about the roughness and the chemical structure of the surface.
The interfacial tension allows conclusions on the chemical and topological properties of coating substrates. The effects of surface cleanliness and effects of surface treatments can be documented.
Beside its use in the coating industry, this measurement method is also used e.g. in microelectronics and wafer production for quality assurance.